
News
Critical skills for checking the quality of your assessment resources.
The purpose of the assessment tool
The main purpose of an assessment tool, student assessment, or assessment pack is to ensure that trainers and assessors can effectively establish whether a learner is competent or not yet competent in a training product. There are three ways a trainer/assessor can establish competence:
- Tell me what you can do (Demonstration of knowledge)
- Show me what you can do (Demonstration of skills)
- Make me something (Application of knowledge and skills)
In order to accomplish this, we will need to establish the following:
Step 1: Understand how the assessment materials meet the training package requirements
This step necessitates you concentrating on how the assessment materials fit the requirements of the training package. This is the step when you understand what competence in this particular unit of competency will look like.
Focus points include understanding of:
- What is the AQF level where the unit of competency will be used?
- What is the unit descriptor/application of the unit saying about work activities included in the unit of competency?
- What are the prerequisite or corequisite requirements related to the unit of competency?
- What level of skill is required for this unit according to where (which qualification) the unit of competency will be used
- What are the elements, performance criteria, range of conditions, foundation skills, knowledge evidence, performance evidence, assessment conditions
- Read the assessment conditions and foundation skills: What are the conditions under which this work activity should be conducted
- Are there any other specific requirements applicable to this unit of competency?
Before moving on to practical task activities, the learner must first demonstrate that he or she understands the subject through demonstration of knowledge.
KNOWLEDGE – you need to have knowledge before you can perform
Look over the requirements for the training package and have a close look at the knowledge evidence to see if it says “once is sufficient.” If it does not state that, it implies that you must address each of the knowledge evidence criteria at least twice. We can address the knowledge evidence requirements using a variety of activities such as questions and answers, case studies, report writing, and other knowledge-based assessment methods.
PERFORMANCE – means that you have to do something
Then it’s time to look at performance criteria and performance evidence, and once again, pay attention to whether or not there are instructions on how many times this should be addressed. If this is not the case, each performance criteria and the performance evidence must be addressed in the assessment tasks and activities at least twice, if not more, utilising a variety of assessment methods and activities such as projects, portfolios, practical task activities, workplace tasks and observations and so on.
Focus on the action verbs and action keywords
Focus on all action verbs and action keywords included in the training package when developing your assessment resources. Each and every action verb and keywords must be addressed through the assessment resources.
Bloom’s taxonomy of measurable verbs is a good starting point to understand more about the action verbs.
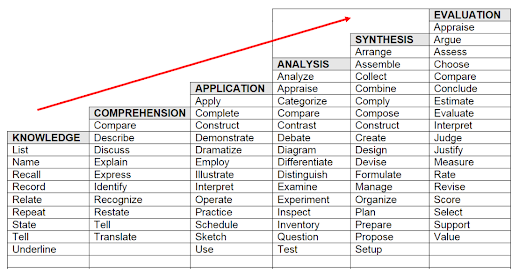
Ensure if something is plural you have addressed them more than once
If there is anything mentioned as plural such as strategies, you must ensure the assessment resources have at least two (2) or more strategies mentioned in them.
You must establish if each component of the training package requires evidence in the form of knowledge, skill or product.
Step 2: Check the content for validity and reliability
Ensure all content is complete, error-free, plagiarism and copyright issues free, you also need to ensure that:
- Assessment resources have sufficient and clear information regarding what, when, how, where, why for your assessment template and all assessment tasks and activities.
- Assessment resources have robust benchmarking and/or trainers’ guidance.
- Assessment resources are allowing the trainer/assessor to assess the skills and knowledge of students through different assessment tasks over a period of time to ensure consistency and sufficiency.
- Each and every question and assessment task has very clear guidelines around what is expected from the students in terms of both quantity and quality.
- You have customised the off-the-shelf resources according to your RTO needs and requirements and not using them as-is.
- Your assessment resources are written by industry experts with subject matter experts and are industry-relevant and current.
- Your assessment resources address all requirements of the training packaging rules
- Your assessment resources have detailed and valid performance checklists/observation checklists for assessing and observing the students before, during and after any skill assessment activity or workplace task
- Your trainers and assessors gather sufficient, valid evidence for competency assessment
- Your organisation offers appropriate simulated environments for conducting assessments
- The authenticity of assessment, particularly in distance and online delivery is established and maintained
- The context and conditions of assessment. For example, an assessment tool is developed to cater for a particular language, literacy and numeracy requirements, the learner’s workplace experience or other learner needs that require reasonable adjustment.
- The context of the assessment may also take into account assessments already completed, and the competencies demonstrated in these assessments. By looking at the context, you can consider the conditions under which evidence for assessment must be gathered.
- All activities are conducted adequately using the required:
- equipment or material requirements
- contingencies
- specifications
- physical conditions
- relationships with team members and supervisors
- relationships with clients/customers
- timeframes for completion.
- Assessment methods or tasks are suitable to the requirements of the units of competency and students are assessed on the tasks and activities according to the requirements of the training package.
- The language used is simple English
- The evidence required to make a decision of competency is clearly outlined
- The types of activities and tasks students need to perform are clearly outlined
- The level of performance required for each assessment activity is clearly outlined
- Adequate exposure to workplace conditions, including appropriate simulated environments, is provided
- Sufficient knowledge-based assessment tasks and activities such as written questions and case studies etc.
- Sufficient practical based assessment tasks and activities such as projects, role plays, workplace tasks and observations etc.
- Assessment resources are error-free and free from any grammar, copyright or plagiarism issues
Step 3: Focus on evidence collection and assessment methods
Focus on evidence collection and assessment methods after ensuring that the assessment resources meet the training package requirements. The focus points should include:
- What are the assessment methods selected for evidence collection?
- Are these suitable and appropriate for evidence collection?
- What are the other methods that may be used for evidence collection?
- Where and how should evidence be collected?
- What resources are required for evidence collection?
Foundation skills, assessment conditions, performance evidence, performance criteria and knowledge evidence should be taken into consideration when designing the evidence collection and assessment methods.
The evidence collection and assessment methods should change according to the AQF level where the units of competency will be used. For example, for a Certificate II, III level true or false, match the following statements with, multiple-choice questions, fill in the blanks might be appropriate but for Certificate IV and Diploma short answer questions, closed book, time-limited exams, contrast and separate, and other assessment methods could be used. We have included an AQF summary for you to understand how each AQF level requires a different set of requirements.
| AQF Level | Summary | Qualifications | Purpose of this Qualification |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Graduates at this level will have knowledge and skills for initial work,
community involvement and/or further learning |
Certificate I | basic functional knowledge and skills to undertake work, further learning and community involvement. |
| 2 | Graduates at this level will have knowledge and skills for work in a
defined context and/or further learning |
Certificate II | qualify individuals to undertake mainly routine work and as a pathway to further learning. |
| 3 | Graduates at this level will have theoretical and practical knowledge and
skills for work and/or further learning |
Certificate III | to qualify individuals who apply a broad range of knowledge and skills in varied contexts to undertake skilled work and as a pathway for further learning. |
| 4 | Graduates at this level will have theoretical and practical knowledge and
skills for specialised and/or skilled work and/or further learning |
Certificate IV | to qualify individuals who apply a broad range of specialised knowledge and skills in varied contexts to undertake skilled work and as a pathway for further learning. |
| 5 | Graduates at this level will have specialised knowledge and skills for
skilled/paraprofessional work and/or further learning |
Diploma | to qualify individuals who apply integrated technical and theoretical concepts in a broad range of contexts to undertake advanced skilled or paraprofessional work and as a pathway for further learning. |
| 6 | Graduates at this level will have broad knowledge and skills for
paraprofessional/highly skilled work and/or further learning |
Advanced Diploma Associate Degree | to qualify individuals who apply specialised knowledge in a range of contexts to undertake advanced skilled or paraprofessional work and as a pathway for further learning. |
| 7 | Graduates at this level will have broad and coherent knowledge and
skills for professional work and/or further learning |
Bachelor Degree | to qualify individuals who apply a broad and coherent body of knowledge in a range of contexts to undertake professional work and as a pathway for further learning. |
| 8 | Graduates at this level will have advanced knowledge and skills for
professional highly skilled work and/or further learning |
Bachelor Honours Degree Graduate and
Vocational Graduate Certificate Graduate and Vocational Graduate Diploma |
to qualify individuals who apply a body of knowledge in a specific context or range of contexts to undertake professional or highly skilled work and as a pathway for research and further learning. |
| 9 | Graduates at this level will have specialised knowledge and skills for
research, and/or professional practice and/or further learning |
Masters Degree | to qualify individuals who apply an advanced body of knowledge in a range of contexts for professional practice and as a pathway for further learning. |
| 10 | Graduates at this level will have a systematic and critical understanding of
a complex field of learning and specialised research skills for the advancement of learning and/or for professional practice |
Doctoral Degree | to qualify individuals who apply a substantial body of knowledge to research, investigate and develop new knowledge, in one or more fields of investigation, scholarship or professional practice. |
You must look for if the assessment methods accurately and properly describe how many questions students must do correctly to be deemed satisfactory in the assessment task or activity and then check mapping to ensure your recommendation does not compromise with the integrity of the assessment.
Always remember that each of the evidence collection and assessment methods must flesh out the details related to the assessment activities and tasks such as what, why, where, how, when something must occur.
Step 4: Language, Literacy and numeracy requirements of the unit
The assessment tool must reflect the language, literacy and numeracy requirements related to the work task and work activities required to be assessed. Your focus points should include:
- Reading
- Writing
- Numeracy
- Oral communication
- Learning
Step 5: Have a comprehensive mapping document
A comprehensive mapping document is required to ensure all training package criteria has been addressed appropriately and comprehensively. Mapping is a cross-referencing activity where each component of the unit of competency is cross-referenced to one or more assessment criteria or questions in the assessment activities and tasks. Mapping is more a ‘content’ validity process and not a ‘process’ validity process.
Step 6: Focus on what kind of customisation is required
Regardless if you have developed the assessment resources in-house or you have purchased them as off-the-shelf resources, you must customise and contextualise each training product.
The customisation and contextualisation should occur in terms of:
- training context,
- learner characteristics,
- delivery modes,
- cultural context,
- technology requirements,
- AQF level,
- intent if the unit of competency is not addressed appropriately,
- formatting,
- grammar,
- Your RTO’s templates and style guides
Step 7: Conduct a pre-validation
Even though this is not a requirement in the standards, we would strongly recommend you validate the assessment tools against all the criteria mentioned in this article.
 1800 961 980
1800 961 980 info@careercalling.com.au
info@careercalling.com.au

























